|
|
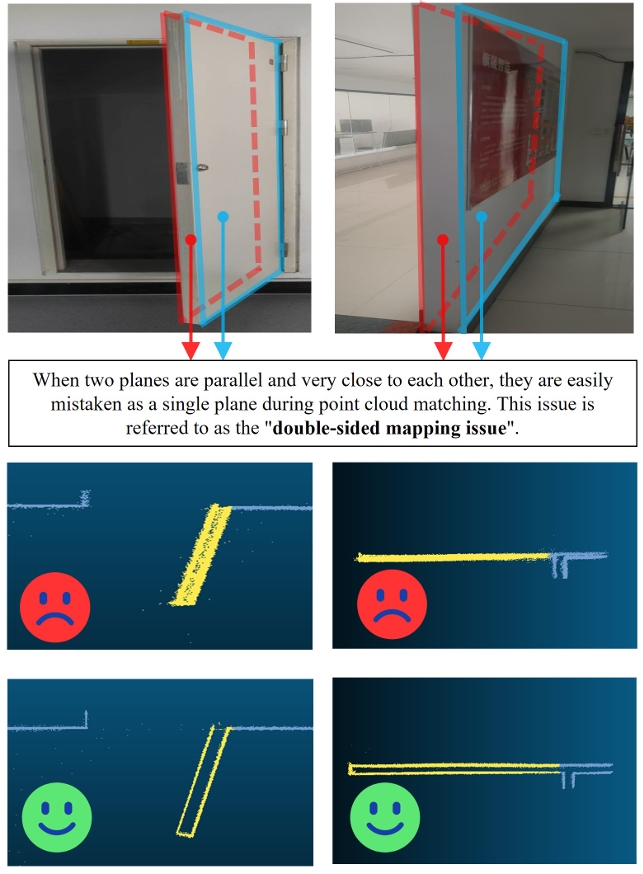
|
II-NVM: Enhancing Map Accuracy and Consistency with Normal Vector-Assisted
Mapping
Chengwei Zhao*, Yixuan Li*, Yina Jian, Jie Xu†, Linji Wang, Yongxin Ma, Xinglai Jin IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L), 2025 [arXiv] [code] II-NVM is a Normal Vector-Assisted Mapping framework that enhance the voxel map structure to store both point cloud data and normal vector information, enabling the system to evaluate consistency during nearest neighbor searches and map updates. This process distinguishes between the front and back sides of surfaces, preventing incorrect point-to-plane constraints. Moreover, we implement an adaptive radius KD-tree search method that dynamically adjusts the search radius based on the local density of the point cloud, thereby enhancing the accuracy of normal vector calculations. To further improve real time performance and storage efficiency, we incorporate a Least Recently Used (LRU) cache strategy, which facilitates efficient incremental updates of the voxel map. |
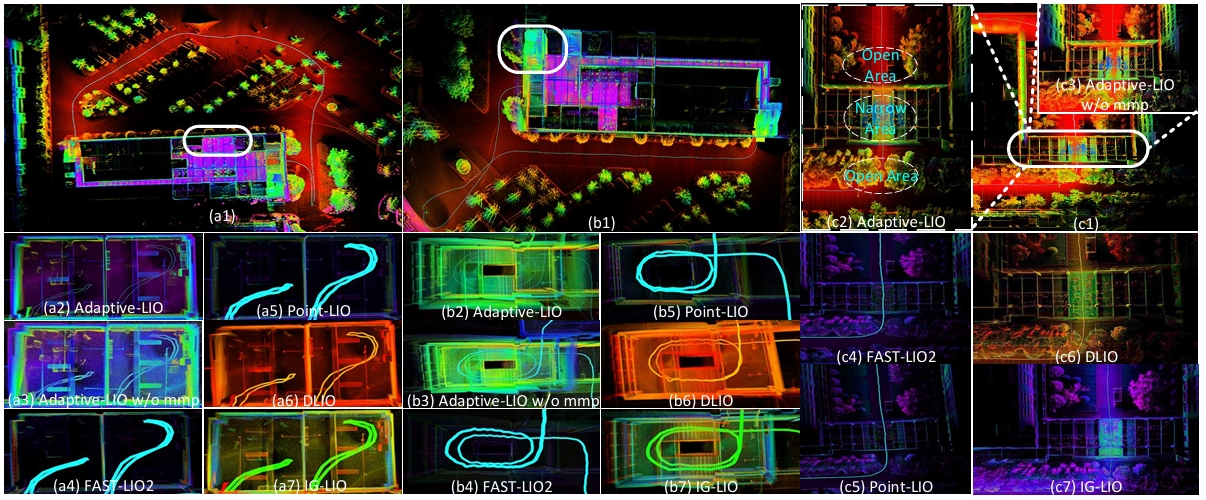
|
Adaptive-LIO: Enhancing Robustness and Precision through Environmental
Adaptation in LiDAR Inertial Odometry
Chengwei Zhao*, Kun Hu*, Jie Xu†, Lijun Zhao†, Baiwen Han, Kaidi Wu, Maoshan Tian, Shenghai Yuan IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024 [paper] [arXiv] [code] Adaptive-LIO is a loosely coupled adaptive LiDAR-Inertial-Odometry, which incorporates adaptive segmentation to enhance mapping accuracy, adapts motion modality through IMU saturation and fault detection, and adjusts map resolution adaptively using multi-resolution voxel maps based on the distance from the LiDAR center. Our proposed method has been tested in various challenging scenarios, demonstrating the effectiveness of the improvements we introduce. |
|
|
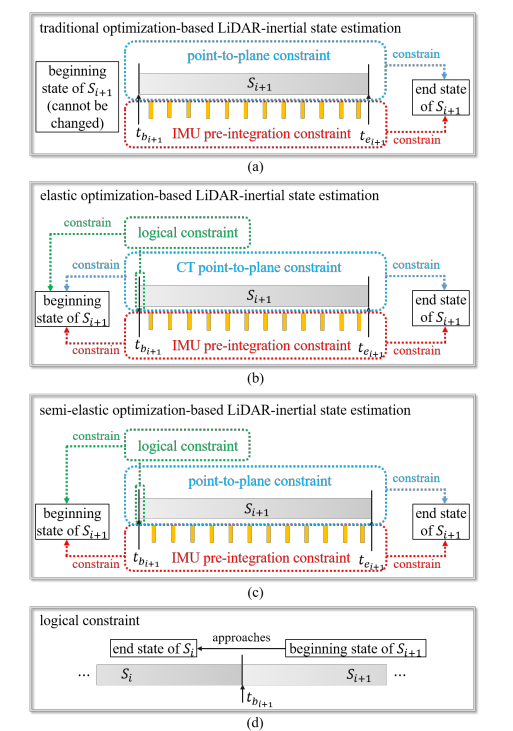
|
Semi-Elastic LiDAR-Inertial Odometry
Zikang Yuan, Fengtian Lang, Tianle Xu, Ruiye Ming, Chengwei Zhao, Xin Yang* IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2025 [paper] [code] Semi-Elastic-LIO (Semi-Elastic LiDAR-Inertial Odometry) is an accurate and robust optimization based LiDAR-inertial odometry (LIO). Compared with the previous work which treats the state at the beginning of current sweep as equal to the state at the end of previous sweep, the Semi-Elastic-LIO provides the state sufficient flexibility to be optimized to the correct value, thus preferably ensuring improved accuracy, consistency, and robustness of state estimation. |

|
I2EKF-LO: A Dual-Iteration Extended Kalman Filter Based LiDAR
Odometry
Wenlu Yu*, Jie Xu*, Chengwei Zhao, Lijun Zhao†, Thien-Minh Nguyen, Shenghai Yuan, Mingming Bai, Lihua Xie IEEE/RJS International Conference on Intelligent RObots and Systems (IROS), 2024 [arXiv] [code] I2EKF-LO is a Dual-Iteration Extended Kalman Filter (I2EKF) and the LiDAR odometry, this approach not only iterates over the observation equation but also leverages state updates to iteratively mitigate motion distortion in LiDAR point clouds. Moreover, it dynamically adjusts process noise based on the confidence level of prior predictions during state estimation and establishes motion models for different sensor carriers to achieve accurate and efficient state estimation. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that I2EKF-LO achieves outstanding levels of accuracy and computational efficiency in the realm of LiDAR odometry. |
|
|
|
|
